

- #SIGNIFICANCE OF FEUDALISM IN THE MIDDLE AGES HOW TO#
- #SIGNIFICANCE OF FEUDALISM IN THE MIDDLE AGES FREE#
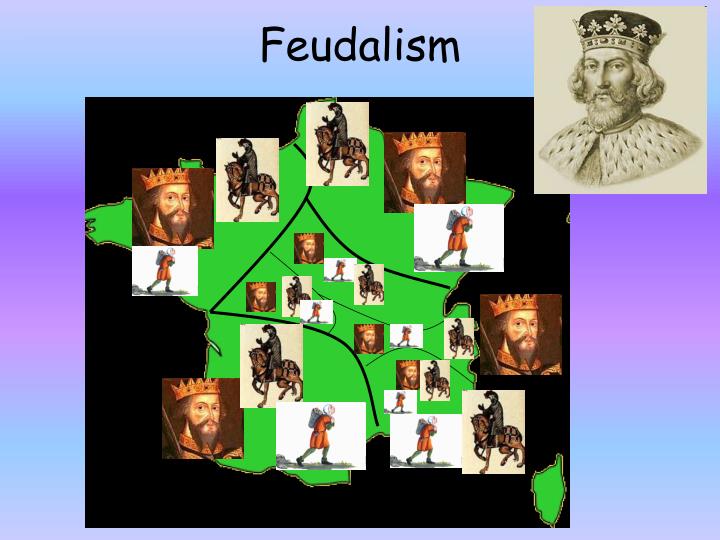
The one law that extended across Europe was the sacred oath of loyalty that a vassal took. Individual lords made their own laws and enforced them in their own fiefs. But there were few laws shared across different kingdoms. These agreements were made public with special ceremonies held in a church and arranged by kings and priests.įeudal loyalties held law and order in place within a kingdom. The links between vassals and lords encouraged people to think of themselves as part of a larger whole.įeudal agreements were meant to last. And, the promises, or oaths, that vassals swore were what held these networks together. Instead there were networks of lords and vassals under the rule of a king. During the Middle Ages there were no nations or central governments in the modern sense. In return, the king promised to protect and support the vassal.įeudal government was not like our modern government. The vassal would swear to fight loyally for the king. And each would make certain promises to the other. The king would give him a large amount of land, called a fief. These kings made deals with powerful leaders, or lords. The system that developed around the most powerful people is called feudalism.įeudalism arose because kings often needed warriors to fight for them. Therefore, the people close to the king, especially the nobility, were the ones who had the most important jobs.

These were the kings, lords, and knights who fought for the kings. The important people in the Middle Ages were those who controlled land. The following is a chart showing the structure of the feudal system. They often battled each other and created a lot of chaos. Feudalism helped establish order by creating a system in which different classes of people supported each other in different ways. There was no strong central government left in Western Europe. The Middle Ages began after the Roman Empire collapsed.
#SIGNIFICANCE OF FEUDALISM IN THE MIDDLE AGES FREE#
Peasants- some free who were carpenters, bakers, blacksmiths, etc., but most were treated likes slaves and lived hard livesįeudalism was a political and military system that provided some stability during the Middle Ages. Serf- a person who was bound to live and work on the land of a noble Vassal- a person who is promised to fight when needed by his lord in exchange for land

Lords- (who were nobles) ran the manor(given by the king), owned the crops, and the peasantsįief- a large piece of land granted by a king to a lord in exchange for his loyalty Manor- farming estate where nobles and serfs lived and worked
It will help you better understand the article that follows: Learning Target: I can interpret the system of feudalism and its impact on the lives of people in the Middle Agesīefore you begin reading, start with the vocabulary. YOU MUST HIT THE SUBMIT BUTTON ON THE ATTENDANCE FORM TO BE MARKED PRESENT EACH DAY. » NYCSA or NYC Schools Account Information for Parents/GuardiansĭON'T FORGET TO DO YOUR DAILY ATTENDANCE TODAY AND EVERYDAY HERE AT IS51.ORG UNDER THE NEWS AND ANNOUNCEMENT SECTION OR ON PUPILPATH.» High Schools & Specialized High School Admissions.» High School Admissions Guide 2022-2023.
#SIGNIFICANCE OF FEUDALISM IN THE MIDDLE AGES HOW TO#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
